ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS
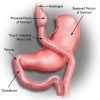
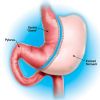
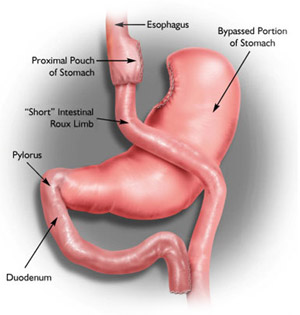 According to the American Society for Bariatric Surgery and the National Institutes of Health, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is the most effective method of weight loss and weight maintenance of all surgical and medical techniques available. It is the most frequently performed weight loss procedure in the United States. In this procedure, stapling creates a small (15 to 20cc) stomach pouch. The remainder of the stomach is not removed, but is completely stapled shut and divided from the stomach pouch.
According to the American Society for Bariatric Surgery and the National Institutes of Health, Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is the most effective method of weight loss and weight maintenance of all surgical and medical techniques available. It is the most frequently performed weight loss procedure in the United States. In this procedure, stapling creates a small (15 to 20cc) stomach pouch. The remainder of the stomach is not removed, but is completely stapled shut and divided from the stomach pouch.
The outlet from this newly formed pouch empties directly into the lower portion of the jejunum, thus bypassing calorie absorption. This is done by dividing the small intestine just beyond the duodenum for the purpose of bringing it up and constructing a connection with the newly formed stomach pouch. The other end is connected into the side of the Roux limb of the intestine creating the "Y" shape that gives the technique its name. The length of either segment of the intestine can be increased or decreased to produce lower or higher levels of malabsorption.
Advantages
The average excess weight loss after the Roux-en-Y procedure is generally higher in a compliant patient than with purely restrictive procedures.
One year after surgery, weight loss can average 77% of excess body weight.
You should be aware that weight loss among a large patient population is highly variable and is due to many reasons aside from the surgery alone.
A 2000 study of 500 patients showed that 96% of certain associated health conditions studied (back pain, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, diabetes and depression) were improved or resolved with weight loss surgery.
Risks
Because the duodenum is bypassed, poor absorption of iron and calcium can result in the lowering of total body iron and a predisposition to iron deficiency anemia. This is a particular concern for patients who experience chronic blood loss during excessive menstrual flow or bleeding hemorrhoids. Women, already at risk f
or osteoporosis that can occur after menopause, should be aware of the potential for heightened bone calcium loss.
Bypassing the duodenum has caused metabolic bone disease in some patients, resulting in bone pain, loss of height, humped back and fractures of the ribs and hip bones. All of the deficiencies mentioned above, however, can be managed through proper diet and vitamin supplements.
A chronic anemia due to Vitamin B12 deficiency may occur. The problem can usually be managed with Vitamin B12 pills or injections.
A condition known as "dumping syndrome" can occur as the result of rapid emptying of stomach contents into the small intestine. This is sometimes triggered when too much sugar, fat, or large amounts of food are consumed. While generally not considered to be a serious risk to your health, the results can be extremely unpleasant and can include nausea, weakness, sweating, faintness and, on occasion, diarrhea after eating. Some patients are unable to eat any form of sweets after surgery.
The bypassed portion of the stomach, duodenum and segments of the small intestine cannot be easily visualized using X-ray or endoscopy if problems such as ulcers, bleeding or malignancy should occur.

About Audencio Alanis M.D.
Dr. Alanis is one of the pioneers of Bariatric Surgery in Houston, Texas.
Today, today 95% of his practice is in Bariatrics and he has performed over 4000 Bariatric cases both open and laparoscopic procedures, including lap bands, roux-en-y, and sleeve gastrectomies.

Weight Problems
Being overweight has many negative implications.
The most serious consequence is the increased risk of illness and death with increasing severity of obesity, but many other areas of life are affected

BMI Calculator
Use our interactive BMI Calculator
Body mass index (BMI) is a measure of body fat based on height and weight that applies to adult men and women. Enter your weight and height to find out your BMI.

Links
Informative links
Click below to access all the information you need to know about Bariatric Surgery